Haven’t heard of SASE before? You’re not alone. Standing for Secure Access Service Edge, SASE is a new buzzword in IT security. This article explains SASE in plain English so anyone can understand it. We’ll cover what it is, why it matters, who needs it, top vendors, deployment considerations, and address common questions. Let’s dive in!
What Does SASE Stand For?
SASE stands for Secure Access Service Edge. It’s a security model that brings together software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN) capabilities with cloud-based security services.
SASE delivers integrated networking and security functions from the cloud to users across an organization. So remote employees, on-site staff, devices, and cloud apps are all protected by one umbrella solution.
How Does SASE Differ from Traditional Security?
In the past, companies relied on a patchwork of different security products – some lived physically on corporate premises, others came from various cloud providers.
SASE changes this by bundling critical networking and security services into one cohesive cloud-based offering. Capabilities like firewalls, threat analysis, data encryption, VPNs, and more all reside in the cloud instead of on-site hardware.
What Are the Core Components of a SASE Architecture?
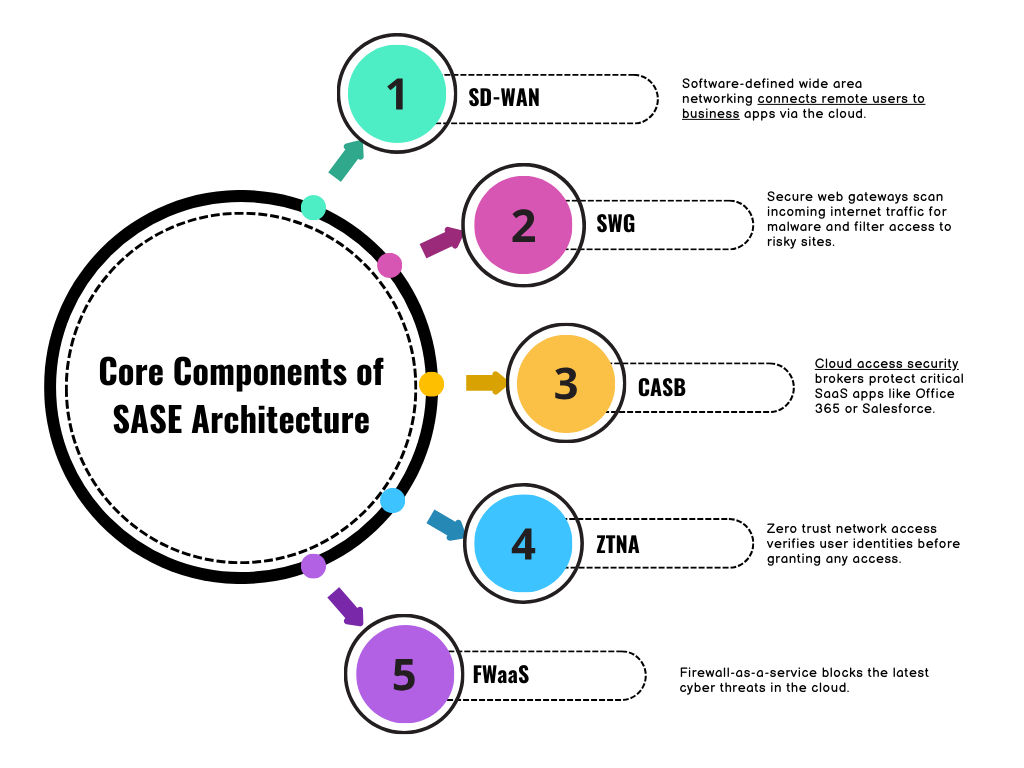
A complete SASE platform contains several key ingredients:
- SD-WAN: Software-defined wide area networking connects remote users to business apps via the cloud.
- SWG: Secure web gateways scan incoming internet traffic for malware and filter access to risky sites.
- CASB: Cloud access security brokers protect critical SaaS apps like Office 365 or Salesforce.
- ZTNA: Zero trust network access verifies user identities before granting any access.
- FWaaS: Firewall-as-a-service blocks the latest cyber threats in the cloud.
By combining these tools natively into one integrated suite, SASE closes security gaps that can come from piecing together standalone products.
What Benefits Does SASE Offer for Businesses?
There are several compelling reasons companies are considering SASE adoption:
- Improved Security Posture: Consolidated tools provide 360-degree protection against modern cyber threats targeting networks, endpoints, and cloud apps.
- Faster Performance: Direct access to applications and data via the cloud minimizes latency issues associated with some VPNs.
- Lower Costs: No expensive hardware to maintain on corporate premises. Cloud delivery allows usage-based pricing.
- Simplified IT Management: One dashboard for networking and security reduces complexity for admins. Vendors handle back-end software updates.
Who Needs SASE Solutions?
Nearly any organization can benefit from SASE capabilities, but it offers particular advantages for:
- Companies with remote, mobile, and hybrid workforces
- Businesses undergoing digital transformation initiatives
- Organizations reliant on SaaS apps like Office 365 or Salesforce
- Distributed enterprises with multiple locations
- Heavily regulated industries like finance, insurance, and healthcare
Leading SASE Vendors to Consider
Major players in the SASE market include VMware, Cato Networks, Cisco, and Palo Alto Networks.
VMware provides extremely robust features focused on large enterprises. Cato excels at threat prevention for small/medium businesses. Cisco and Palo Alto land in the middle with solid capabilities for moderate pricing.
Common Challenges When Implementing SASE
While promising, adopting SASE introduces certain changes that may prove difficult:
- Integrating Existing Systems: Old networks and firewalls must connect and sync properly with SASE’s cloud infrastructure.
- Compatibility Issues: Some legacy on-prem apps and tools won’t interface well with new SASE software.
- Learning Curves: Employees will require extensive retraining on updated security protocols.
- Cost Overruns: Moving too quickly can drive up expenses past initial budgets.
What Are Best Practices for SASE Success?
Careful planning and execution can help overcome these hurdles:
- Audit existing infrastructure to uncover compatibility gaps.
- Phase in solutions slowly department by department.
- Set aside adequate training time and budget.
- Compare multiple vendors to find optimal fit.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
SASE delivers integrated networking and security from the cloud to users everywhere. It promises improved protection, faster performance, and lower costs compared to legacy models. Leading options come from VMware, Cato, Cisco, and Palo Alto. Methodical evaluation and deployment helps maximize benefits while minimizing disruption across organizations.
FAQs
SASE = Secure Access Service Edge
No. SASE incorporates SD-WAN as a component but also includes security tools like SWG, CASB, ZTNA, and FWaaS.
Leading vendors include VMware, Cato, Cisco, Palo Alto Networks. Many smaller providers exist too.
Not necessarily. SASE often complements parts of the existing stack. Hybrid deployments are common.
Distributed organizations like retail chains, manufacturers, financial services firms, hospitals, and insurers.
